Prevention
Brushing
When does it start?
Start brushing your child’s teeth at the age of one. It has been proven that when teeth brushing begins at this age the child will suffer less from dental decay. This occurs since early tooth brushing habit can diminish the number of bacteria from the very first stages of the child’s development, and maintain a low concentration of bacteria throughout life.
Age 1-2: use a minimum amount of fluoridated toothpaste (lentil-sized) on the child’s toothbrush. It does not matter if your child swallows a bit of toothpaste.
Age 2-6: when your child becomes 2 years old, use a pea-sized amount of toothpaste. For more effective brushing do not make your child rinse his mouth with water after brushing.
Age 6 and above: a normal amount of toothpaste should be used provided that he can spit it out at ease. The use of toothpaste is necessary due to the beneficial effect of the fluoride on the enamel of the teeth.
Before the age of six encourage your child to avoid rinsing the toothpaste. it has been proved that the beneficial effect of the toothpaste is increased if the child does not rinse with water after brushing.
 Please remember the following:
Please remember the following:
Bacteria must be removed twice a day (morning and night) since they begin to develop 12 hours after their removal.
Parents must brush their child’s teeth till the age of 8 – 10. Research shows that children upto this age cannot clean their teeth correctly on their own.
Toothpaste must contain an adequate amount of fluoride according to the child’s age. We will advise you on this topic during your child’s first visit.
Too much toothpaste on the brush during the years 1-6 can cause damage on the permanent teeth due to increased swallowing of Fluoride that it is in the toothpaste .If this happens then Fluorosis can occur. Fluorosis is a disease of the enamel which occurs during the development of the permanent dentition and presents with white – brown lesions on the enamel of the permanent teeth.
Brushing with an electric toothbrush is just as good as a manual toothbrush.
Toothbrush’s with a small head, toothbrush’s with nylon bristles and bent handles are very good for your child.
You need to change your brush frequently, every 3-4 months, due to accumulation of bacteria and the damaged bristles. Do not keep using toothbrushes like the one in the picture since they do more harm than good (abrasions of the gums, attrition of the teeth, compromised cleaning).
Find more information on www.cspd.com.cy
Dental floss
Brushing alone is not enough to remove bacteria since it only cleans 3 out of the 5 surfaces of the teeth. Dental floss should be used every night after brushing. It helps prevent dental decay at the proximal surfaces of the teeth. Also, flossing significantly decreases bad breath since it eliminates the bacteria which are trapped between the teeth or the fillings. Waxed dental floss is softer and usually more acceptable by children.
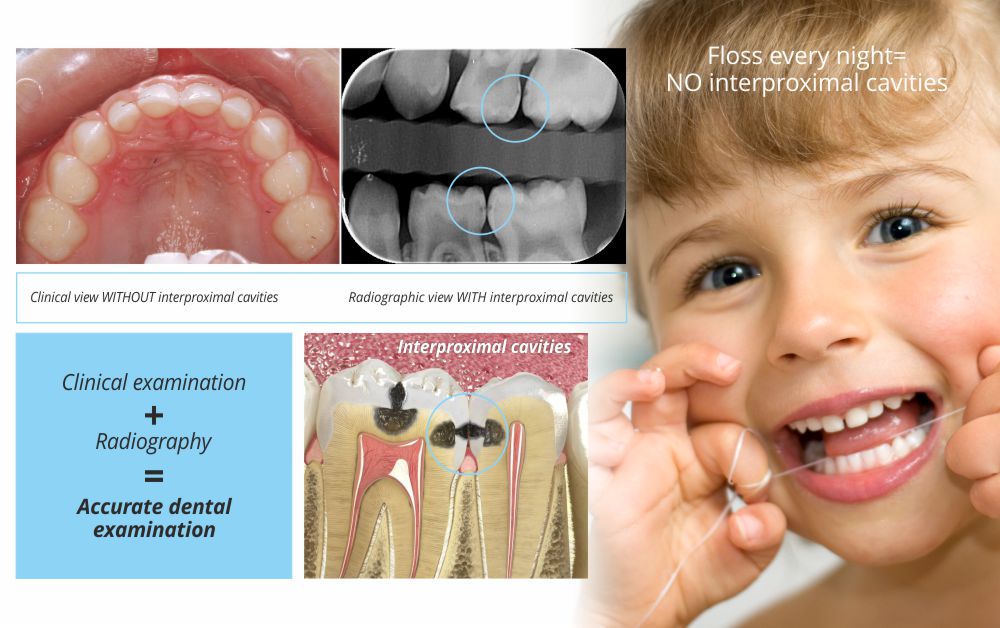
Antiseptic mouth rinse
Helps in eliminating bacteria, reduces gingivitis and dental decay. It should only be used on the recommendation of the Dentist. It does not substitute brushing and flossing but compliments a treatment where required. A good mouthwash can reduce significantly bad breath by decreasing the number of bacteria that are responsible for bad breath.
However, some types of mouth rinses can stain the teeth after frequent use and can even cause a metallic taste. Some other mouth rinses can cause resistant microbial strains. For these reasons, the mouth rinses should be recommended by the Dentist! We can help you choose the right mouth rinse.
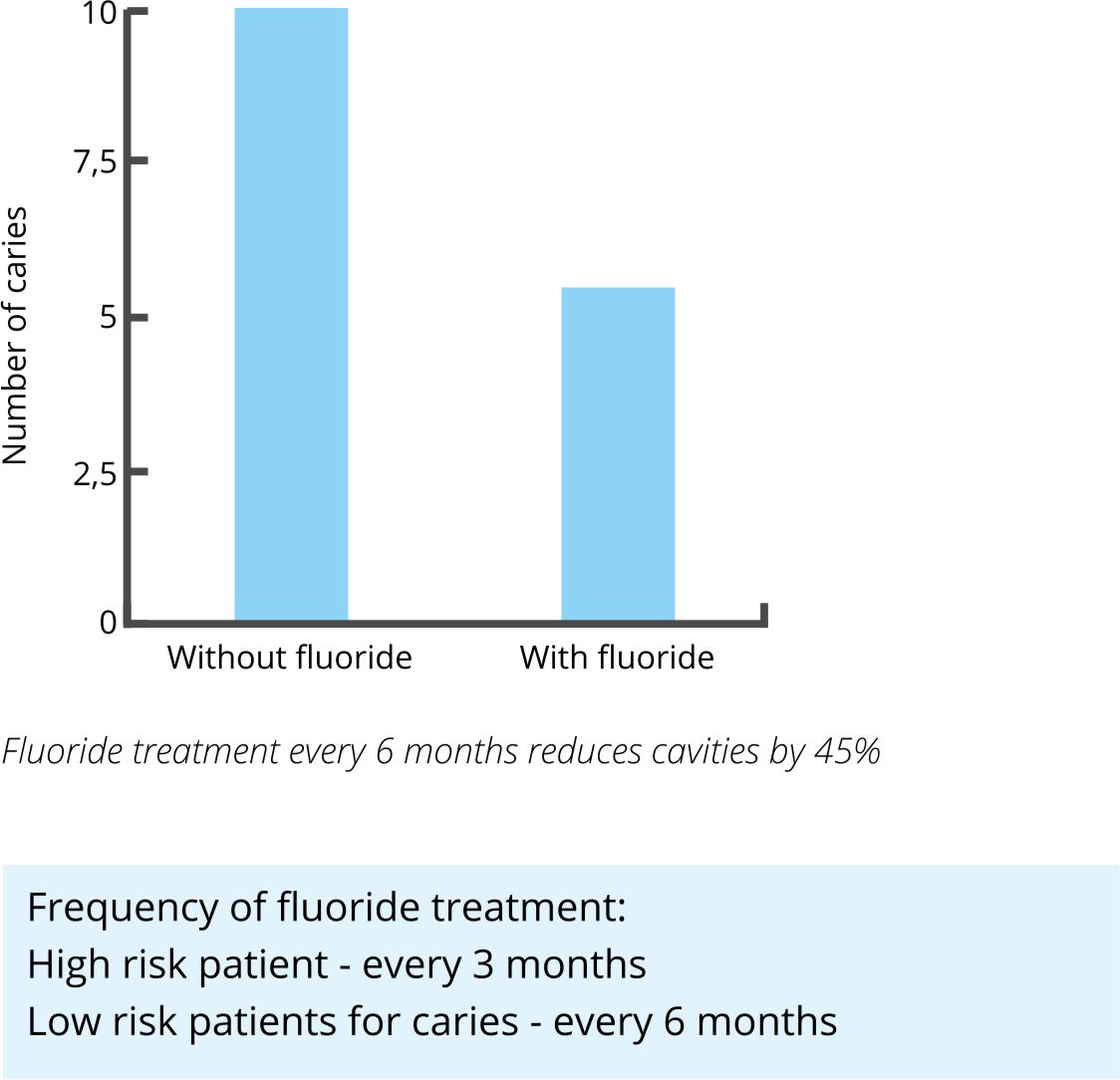
Fluoride
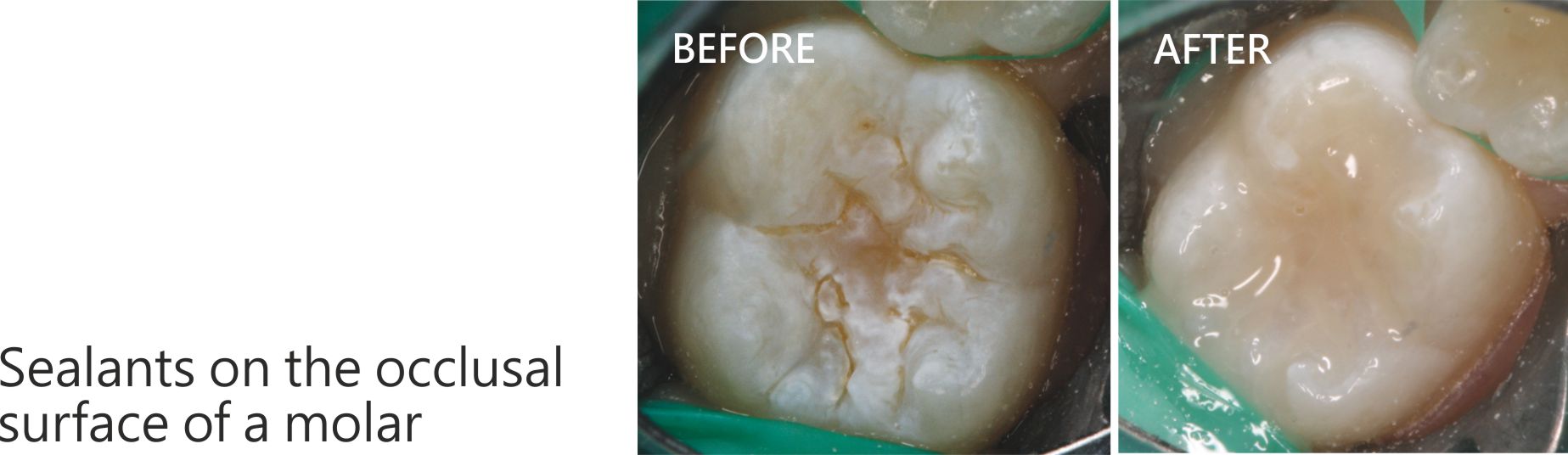
Preventive sealants
When? Why?
When the first permanent molars erupt around the age of six years, they should be evaluated for possible sensitivity to dental caries for the reasons below;
- When a permanent molar erupts in the mouth, the enamel of the tooth is soft and porous initially but within time it absorbs elements (calcium, phosphorous) from the saliva and hardens. This process takes up to 5 years after the tooth erupts in the mouth. During these 5 years the permanent teeth are very vulnerable to dental caries.
- Anatomically, these teeth have multiple narrow and deep grooves and pits which easily collect food debris and bacteria (picture 1).
- Young children have difficulty in cleaning these teeth due to their anatomy and their posterior position. Sometimes kids never brush these teeth at all.
For the above 3 reasons and based on the child’s caries risk, it is advised to seal these grooved with preventive fillings.
What are they? How do they benefit your teeth?
- Sealants are white or clear fillings which are placed in the pits and fissures of the molars in order to eliminate the accumulation of food and microbial plaque on the occlusal surfaces of these teeth.
- Sealants are placed on healthy teeth – before they become carious – without necessarily removing any tooth structure.
- When sealants are placed, it has a liquid consistency so that it flows into the narrow grooves of the teeth. Later on, the Dentist uses a special light curing device which hardens the material.
- Their life span on the teeth ranges from 4-6 years.
- Sealants protect the teeth 100% against any cavities.
- During the routine examination of the child, the sealants are monitored and if needed we re-apply. Broken, missing or worn off sealants are dangerous to the teeth since they act as microbial traps.
- Sealants are placed only on the occlusal surfaces of the teeth. We cannot place these on the smooth surfaces of the teeth and thus they do not protect the tooth completely from dental caries.
- According to research in the US, 85% of dental decay occurs on the occlusal surface of the teeth, therefore the preventive benefit of them is significally high.
Conclusion: The placement of preventive sealants is recommended mainly for high risk patients who have a sensitivity to dental caries.
Nutrition
What are the basic causes of a cavity?
A cavity is a type of bacterial disease which is essentially caused with the combination of the following four basic factors.
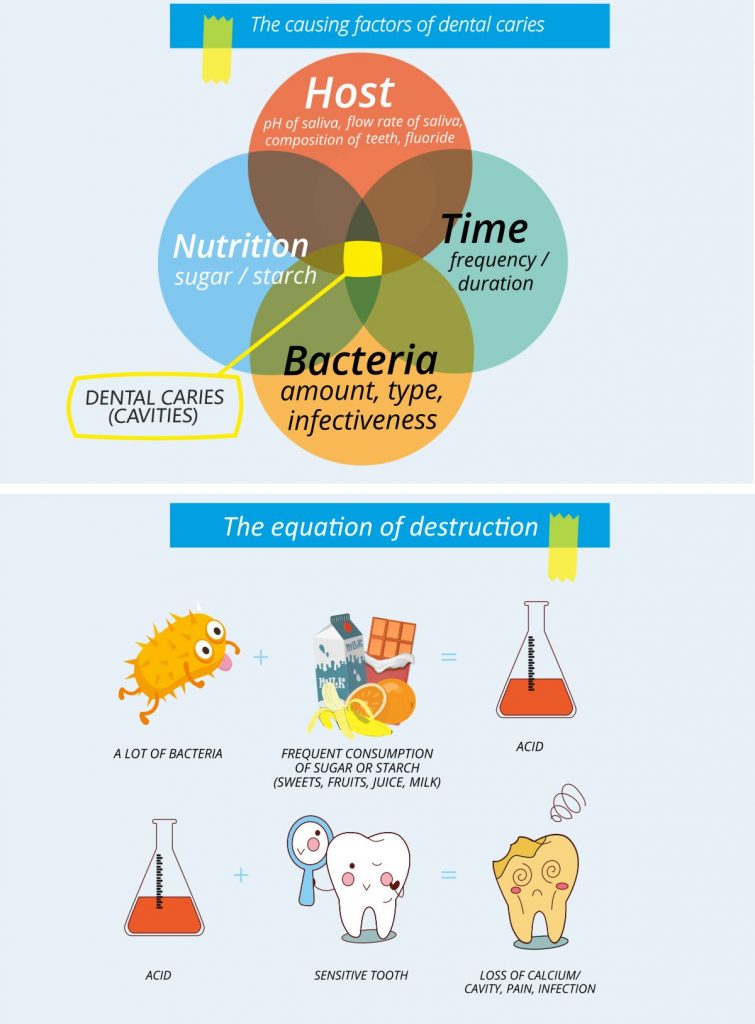
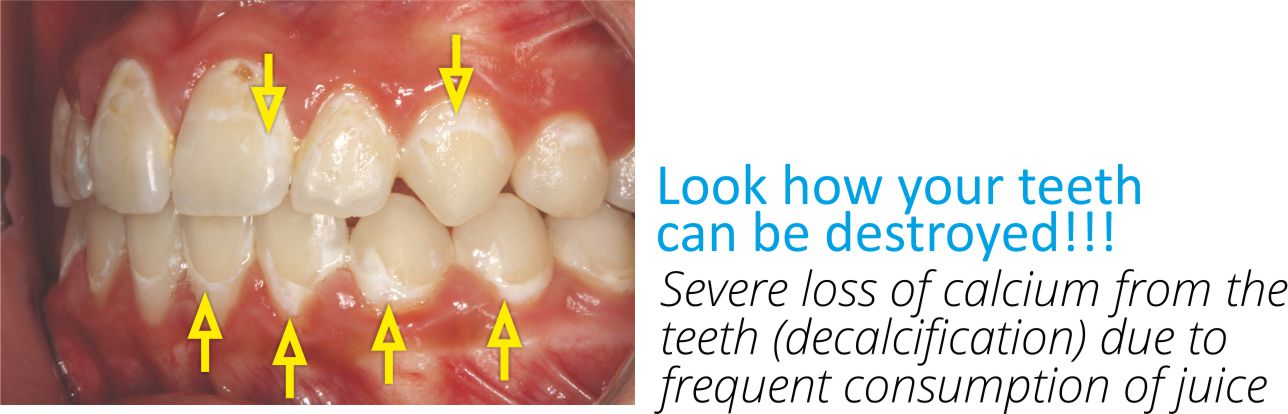
According to the above diagrams, the frequent consumption of foods which are high in sugar, as well as sugary drinks, increase the production of acids which in turn destroy the calcium from the teeth. As a result, this destruction causes decalcifications on the teeth (see photo) and caries will occur.
Learn how to read labels!
Before you grab a snack (in between meals), ask yourself the following; What does this snack contain? Does it have a lot of sugar? Does it stick to your teeth? Is it acidic? If so, rethink your choice! There are healthier snack choices for your teeth. Keep in mind that certain types of sugary foods and drinks are worse than the other.

Juices
An official announcement from the American Pediatric Association which took place in 2017, has concluded that although juices have some nutritional benefits, they are harmful due to their high sugar concentration and due to the lack of proteins and fibres which are found in fruits. Juices lead to an increase in body weight, possible caries and do not provide any nutritional benefit compared to whole fruits. This is applicable to children under the age of one, and also to older children.
The sad truth about sodas
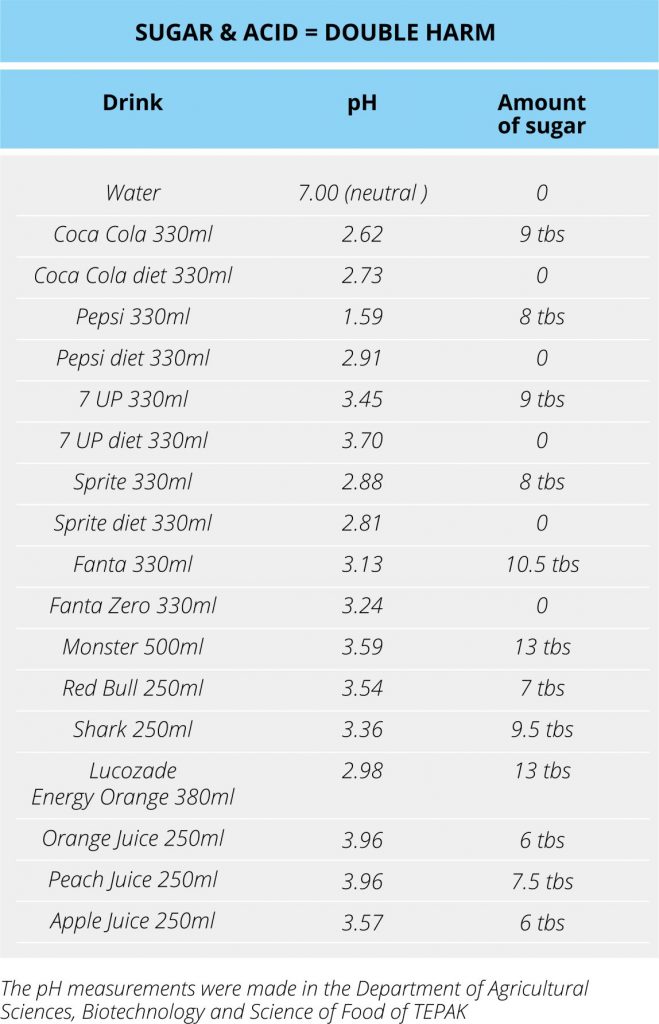
* Soft drinks, energy drinks and fruit juices usually contain high amounts of sugar and have a very low pH (2,5-3,5). This means that they are very acidic (see table).
* Diet soft drinks do not contain sugar; however, they are very acidic.
* 40 years ago, a bottle of soft drink contained 150ml whereas now a bottle contains 330ml and it is not unusual to see 500ml bottles.
* Larger bottle of soft drink contain much more sugar and are even more acidic.
* Soft drinks have been associated with the development of diabetes, obesity and osteoporosis.
How to reduce the risk of cavities;

How to reduce the risk of cavities;
- Do not sip on soft drinks or on juices because this increases the amount of acids in your saliva.
- If you drink soft drinks, use a straw in order to keep the sugar away from your teeth.
- Rinse your mouth with water after drinking soft drinks in order to dissolve the sugar.
- Never drink soft drinks before going to bed without brushing your teeth.
- If you are thirsty, drink water and not soft drinks.
- Visit your dentist regularly.
- Brush your teeth twice a day with the appropriate fluoride based toothpaste, and floss your teeth every night.
- Preventive sealants protect the occlusal surfaces of the teeth and not the smooth surfaces where the acids usually act.