Injured teeth – First Aid – Emergency Cases
First aid for injured teeth
General
Trauma to the teeth are very common and are reported millions of cases worldwide. They particularly occur in children whose upper front teeth are extruding from the mouth. After a trauma occurs, the first feeling a parent and the child have is panic, so our advise is to remain calm and make the following observations before you even call the Dentist:
- Detect if the child has any symptoms like dizziness, vomiting or fainting. In case your child does not feel well, you should call your Paediatrician.
- Also if your child had this injury outside the house, check if his tetanus vaccination is up-to-date.
- Observe for any swelling or abrasions inside and outside the mouth. In case of swelling on the lips or cheeks use an ice pack covered with a cotton towel for few minutes to diminish swelling. Afterwards, call your Dentist.
Broken teeth
If after the trauma, you notice that a part of an anterior tooth is missing look to find it and put it in a cup of milk. This broken part can be reattached to the tooth. If the fractured part of the tooth is not found, an artificial one can be made and attached to the tooth with very good aesthetic result. It is not necessary to reattach the broken part of the tooth the same day – it is alright to wait a few days without any problem occurring. However, it is best to have the tooth examined the same day by the Dentist in case that there is a deep fracture that results in pulp exposure. In this case, a preventive measure should be taken in order to avoid having infection to the nerve of the tooth since it can come in direct contact with the environment.
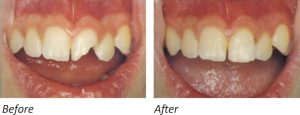
NOTE: The reattachment of a broken tooth can be done only on permanent teeth, NOT ON PRIMARY TEETH.
COMPLICATIONS: In some cases, there is a chance for the nerve to become necrotic and a nerve canal treatment will be needed. All other complications are rare in such trauma cases.
Loosening of the tooth
If your child’s tooth becomes loose but does not change its’ position, and depending on the mobility of the tooth, your Dentist may have to immobilize it. Immobilization is best to be done the same day of the injury.
If the tooth changed position it should be repositioned and immobilized in the correct way, on the same day of emergency before the tooth stays mobilized in the wrong position.
NOTE: Usually only permanent teeth are immobilized but sometimes primary teeth are also good candidates if the Dentist considers that it is the right thing to do. This depends on the age and cooperation of the child, and also the degree of mobility of the tooth.
Intrusion of a primary tooth
Many times after falling on a hard surface, your child’s anterior tooth can move upwards (intrude) and as a result the tooth looks smaller as if a piece of the tooth got chipped, or the tooth can even disappear into the gums. This type of trauma is called intrusion.
TREATMENT: the most common type of treatment is patience. In most cases the tooth which is intruded will slowly emerge and go back to its’ original position within the first 4 months without any complications.
COMPLICATIONS: In some cases, and depending on the severity of the trauma, the tooth can be stuck in the sunken position (ankylosed). If this occurs, the tooth must be extracted since it will prevent the eruption of the permanent successor tooth.
The nerve of the ankylosed tooth may become necrotised and as a result the tooth turns black. Necrotic teeth often lead to infections and sometimes can form abscesses. In such cases, the tooth is destroyed during the time of extraction.
Intrusion of a primary tooth causes a violent movement upwards where the permanent tooth is located. Depending on the upward direction of the primary tooth, the permanent tooth can become hurt since it is located right under it. If this happens, the successor tooth may erupt with a yellow or white spot on its’ surface. A more serious but unusual complication is the change of eruption position of the permanent tooth or even ankylosis.
Dislocation of a permanent tooth
Dislocation of a permanent tooth means that the tooth came out whole from the mouth (crown & root)
This is the most urgent case in Dentistry. If your child gets injured and his whole tooth falls out then proceed as follows:
Call your Dentist
Find the tooth. Make sure that you are holding the tooth from the white – square surface (crown) and not from the root – long and narrow surface with a darker colour. This way we are sure that the root cells are vital in order to have a successful repositioning of the tooth.
If your child cooperates with you, and you have the courage, try placing the tooth back in the periodontium so that the root is kept wet with the blood and to preserve the vitality of the root cells. Hold the tooth in place with your fingers.
Otherwise, store the tooth in a cold glass of milk and bring it immediately to the Dentist. The sooner the repositioning takes place, the better it is. Research shows that if the tooth is repositioned within the first 30-40 minutes, the success rate of implantation is greater.
COMPLICATIONS: they are common and serious and consist of the tooth nerve becoming necrotic, resorption of the root leading to premature loss of tooth, ankylosis of the tooth to the bone, etc.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Primary teeth are not repositioned since there is a very low success rate and a high risk of injuring the successive permanent teeth below.
Complications in newly injured primary teeth
Various complications may occur depending on the severity of the trauma. Even mild trauma can cause complications. Generally, loose or dislocated teeth present more complications than broken teeth.
Necrosis of the nerve of the tooth. In this case, the tooth may begin to darken in color either immediately or at a later time. In any case, the grayish color indicates a 50% chance of the tooth nerve being necrotic and the therapy that should be provided consists of a root canal, when it comes to permanent teeth. When it comes to primary teeth, necrosis with infection is treated either by a root canal or an extraction depending on various factors. However, in primary teeth, the grayish color can sometimes be temporary and the tooth can regain its’ normal color within 4 months, starting from the day of injury. This is a good sign and no other type of treatment is required, except from monitoring the tooth.
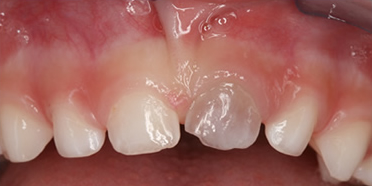
Note that close monitoring is necessary in the case of an injured primary tooth due to the possibility of negatively affecting the successor permanent tooth.
Other complications that may occur:
- Remineralization of the root cavity – the tooth becomes yellow in color – do not worry
- Permanent relaxation of the tooth and early fall
- Root resorption and early fall
Complications of injured teeth
Emergency cases
Toothache: pain which occurs after cold drink, hot drink or food impaction
When your child feels pain after a meal, especially after eating some type of sweet this may indicate that your child may have a tooth with a deep cavity, close to the nerve of the tooth.
What you have to do: tell your child to brush the tooth and to remove any remaining food that has been trapped in the cavity by using a toothpick or dental floss. Bring your child without any delay to the Dental clinic for a check-up and for appropriate dental treatment.
When pain is caused by food impaction, the tooth usually requires a simple filling. However, if you ignore any symptoms and the pain reoccurs, this will result in a more intense and spontaneous pain. Then, a more complicated and time-consuming treatment will take place such as a root canal or an extraction.
Intense, spontaneous pain / pain during the night:
If the pain is spontaneous, meaning that it is caused without chewing or drinking anything, then the condition is more severe. This means that the cavity is very deep and close to the nerve of the tooth and thus the nerve is inflamed.
What you have to do: Give the child a strong anti-inflammatory medication and give us a call. The treatment that we will choose in cases of strong and spontaneous pain is to remove the nerve of the tooth (root canal) which is undergoing inflammation or even extraction of the tooth, depending on various Dental factors.
Toothache upon mastication
In case of a toothache solely upon mastication forces, then the tooth may present with an abscess. Usually, an abscess appears at the end of the tooth, inside the bone, and may not be evident with a naked eye. Because the abscess (red arrow on the picture) is an accumulation of pus (thick liquid), when the patient is chewing the tooth is moving towards the bone and pain occurs. Also, the tooth may become loose or the patient may feel that the tooth is at a higher level than the rest of the teeth.
What you have to do: You need to call us the same day. An abscessed tooth can spread its infection to the surrounding soft tissue of the face and cause swelling of the lips and cheeks. In children this swelling may quickly expand towards the eye or the pharynx and if remained untreated it can cause serious infection to the brain, closure of the larynx and suffocation.
We will examine and provide the appropriate treatment to your child but surely, in cases like these, antibiotics are necessary to stop the course of infection.